Ixodes
| Ixodes Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Ixodes ricinus, engorged | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Ixodida |
| Family: | Ixodidae |
| Genus: | Ixodes Latreille, 1795 [1] |
| Type species | |
| Acarus ricinus | |
| Species | |
|
274 extant, 2 extinct, see text. | |




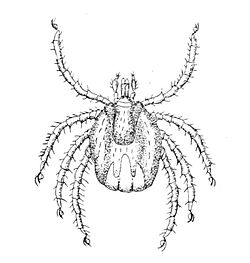
Ixodes is a genus of hard-bodied ticks (family Ixodidae). It includes important disease vectors of animals and humans (tick-borne disease), and some species (notably Ixodes holocyclus) inject toxins that can cause paralysis. Some ticks in this genus may transmit the pathogenic bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi[3] responsible for causing Lyme disease. Additional organisms that may be transmitted by Ixodes are parasites from the genus Babesia, which cause babesiosis, and bacteria from the related genus Anaplasma, which cause anaplasmosis.
Ecology and distribution
[edit]Ixodes species have a cosmopolitan distribution, being found across all major biogeographic realms, including Antarctica, being found on seabirds and in penguin rookeries. The genus parasitises a wide range of mammal, bird and reptile hosts across the world, although rodents and passerine birds are the most common hosts, especially in the Americas.[4]
Description and systematics
[edit]Ixodes is the sole representative of the Prostriata clade of the Ixodidae. Prostriate ticks are distinguished from the Metastriata with reference to the position of the anal groove. In Ixodes species, the groove loops anterior to the anus, whereas in Ambloymma, for example, the groove is positioned posterior to the anus. Ixodes species are small to medium-sized ticks, with a usually pyriform (pear-shaped) or ovate body profile. Mouthparts are anterior in both sexes, but usually long and slender in females, and short in males. Males have sclerotised adanal plates. Ixodes species are eyeless.[5]
| Ixodidae cladogram after Barker et al., (2024)[6] |
Taxonomy
[edit]Ixodes contains 274 species.[7] Classification, recognition and phylogenetic resolution of the Ixodes subgenera is ongoing. As many as 24 subgenera have been recognised by different authors. All are included here for completeness.[8][9][10]
Subgenera
[edit]- Afrixodes Morel, 1966[11]
- Alloixodes Černý, 1969[12]
- Amerixodes Morel, 1998[13]
- Australixodes Barker & Barker et al., 2023[14]
- Ceratixodes Neumann, 1902[15]
- Coxixodes Schulze, 1941[14]
- Endopalpiger Schulze, 1935[16]
- Eschatocephalus Frauenfeld, 1853[17]
- Exopalpiger Schulze, 1935[18]
- Filippoviella Apanaskevich, Greiman, Fedorov, Ahmed & Barker[19]
- Haemixodes Kohls & Clifford, 1967[20]
- Indixodes Morel, 1998[13][21]
- Ixodes Latreille, 1795[8]
- Ixodiopsis Filippova (1957)[22][23]
- Lepidixodes Schulze, 1935[24]
- Monoindex Emelyanova & Kozlovskaya, 1968[25][26]
- Multidentatus Neumann, 1904[27]
- Partipalpiger Hoogstraal et al., 1973[28]
- Pholeoixodes Schulze, 1942[29]
- Pomerantzevella Feider, 1965[30][31]
- Scaphixodes Schulze, 1941[32]
- Sternalixodes Schulze, 1935[8]
- Trichotoixodes Reznik, 1961[33]
- Xiphixodes Schulze, 1941[34]
Species
[edit]- Ixodes abrocomae Lahille, 1916
- Ixodes (Ixodes) abramovi Apanaskevich, 2024[35]
- Ixodes acer Apanaskevich & Schenk, 2020[36]
- Ixodes acuminatus Neumann, 1901
- Ixodes (Indixodes) acutitarsus (Karsch, 1880)
- Ixodes affinis Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes albignaci Uilenberg and Hoogstraal, 1969
- Ixodes (Ixodes) algericus Keskin, Aftisse and Apanaskevich, 2024[37]
- Ixodes alluaudi Neumann, 1913
- Ixodes amarali Fonseca, 1935b
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) ambohitantelensis Englert, Goodman & Apanaskevich, 2023[38]
- Ixodes amersoni Kohls, 1966
- Ixodes (Australixodes) anatis Chilton, 1904
- Ixodes andinus Kohls, 1956a
- Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) angustus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes antechini Roberts, 1960
- Ixodes apronophorus Schulze, 1924
- Ixodes arabukiensis Arthur, 1959
- Ixodes arboricola Schulze and Schlottke, 1929
- Ixodes arebiensis Arthur, 1956c
- Ixodes ariadnae Hornok, 2014
- Ixodes asanumai Kitaoka, 1973
- Ixodes aulacodi Arthur, 1956c
- Ixodes auriculaelongae Arthur, 1958 [39]
- Ixodes auritulus Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes (Endopalpiger) australiensis Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes baergi Cooley and Kohls, 1942
- Ixodes bakeri Arthur and Clifford, 1961
- Ixodes banksi Bishopp, 1911
- Ixodes (Endopalpiger) barkeri Barker, 2019[40]
- Ixodes bedfordi Arthur, 1959
- Ixodes bequaerti Cooley and Kohls, 1945
- Ixodes berlesei Birula, 1895
- Ixodes bivari Santos Dias, 1990
- Ixodes bocatorensis Apanaskevich and Bermúdez, 2017
- Ixodes boliviensis Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes brewsterae Keirans, Clifford and Walker, 1982
- Ixodes browningi Arthur, 1956
- Ixodes brumpti Morel, 1965
- Ixodes brunneus Koch, 1844[41]
- Ixodes calcarhebes Arthur and Zulu, 1980
- Ixodes caledonicus Nuttall, 1910
- Ixodes canisuga Johnston, 1849
- Ixodes capromydis Černý, 1966
- Ixodes catherinei Keirans, Clifford and Walker, 1982
- Ixodes cavipalpus Nuttall and Warburton, 1908
- Ixodes ceylonensis Kohls, 1950
- Ixodes chilensis Kohls, 1956
- Ixodes colasbelcouri Arthur, 1957
- Ixodes collaris Hornok, 2016
- Ixodes collocaliae Schulze, 1937
- Ixodes columnae Takada and Fujita, 1992
- Ixodes conepati Cooley and Kohls, 1943
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) confusus Roberts, 1960[42]
- Ixodes cookei Packard, 1869
- Ixodes cooleyi Aragão and Fonseca, 1951
- Ixodes copei Wilson, 1980
- Ixodes cordifer Neumann, 1908
- Ixodes cornuae Arthur, 1960c
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) cornuatus Roberts, 1960
- Ixodes cornutus Lotozky, 1956
- Ixodes corwini Keirans, Clifford and Walker, 1982
- Ixodes crenulatus Koch, 1844
- Ixodes cuernavacensis Kohls and Clifford, 1966
- Ixodes cumulatimpunctatus Schulze, 1943
- Ixodes dampfi Cooley, 1943
- Ixodes (Trichotoixodes) daveyi Nuttall, 1913
- Ixodes dawesi Arthur, 1956
- Ixodes dendrolagi Wilson, 1967
- Ixodes dentatus Marx, 1899
- Ixodes dicei Keirans and Ajohda, 2003
- Ixodes diomedeae Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes diversifossus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes djaronensis Neumann, 1907
- Ixodes domerguei Uilenberg and Hoogstraal, 1965
- Ixodes downsi Kohls, 1957
- Ixodes drakensbergensis Clifford, Theiler and Baker, 1975b
- Ixodes eadsi Kohls and Clifford, 1964
- Ixodes eastoni Keirans and Clifford, 1983
- Ixodes eichhorni Nuttall, 1916
- Ixodes eldaricus Dzhaparidze, 1950a
- Ixodes elongatus Bedford, 1929
- Ixodes eudyptidis Maskell, 1885
- Ixodes euplecti Arthur, 1958[39]
- Ixodes evansi Arthur, 1956
- Ixodes (Exopalpiger) fecialis Warburton and Nuttall, 1909
- Ixodes (Ixodes) festai Arthur, 1961[43][44]
- Ixodes filippovae Černý, 1961
- Ixodes fossulatus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes (Trichotoixodes) frontalis (Panzer, 1798)
- Ixodes fuscipes Koch, 1844a
- Ixodes fynbosensis Apanaskevich, Horak, Matthee and Matthee, 2011
- Ixodes galapagoensis Clifford and Hoogstraal, 1980
- Ixodes (Filippoviella) ghilarovi Filippova and Panova, 1988b
- Ixodes gibbosus Nuttall, 1916
- Ixodes giluwensis Apanaskevich & Schenk, 2020[36]
- Ixodes goliath Apanaskevich and Lemon, 2018[45]
- Ixodes granulatus Supino, 1897
- Ixodes gregsoni Lindquist, Wu and Redner, 1999
- Ixodes guatemalensis Kohls, 1956
- Ixodes hearlei Gregson, 1941
- Ixodes heathi Kwak, 2018[46]
- Ixodes heinrichi Arthur, 1962
- Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) hexagonus Leach, 1815
- Ixodes himalayensis Dhanda and Kulkarni, 1969
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) hirsti Hassall, 1931
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) holocyclus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes hoogstraali Arthur, 1955
- Ixodes howelli Cooley and Kohls, 1938
- Ixodes hyatti Clifford, Hoogstraal and Kohls, 1971
- Ixodes hydromyidis Swan, 1931
- Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) hunanensis Apanaskevich & Duan, 2022[47]
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) hyracis Apanaskevich, Drew & Pienaar, 2025[48]
- Ixodes inopinatus Estrada-Peña, Nava and Petney, 2014
- Ixodes jacksoni Hoogstraal, 1967
- Ixodes jellisoni Cooley and Kohls, 1938
- Ixodes jonesae Kohls, Sonenshine and Clifford, 1969
- Ixodes kaiseri Arthur, 1957
- Ixodes kandingensis Guo, Sun, Xu and Durden, 2017
- Ixodes kashmiricus Pomerantzev, 1948
- Ixodes kazakstani Olenev and Sorokoumov, 1934
- Ixodes kerguelenensis André and Colas-Belcour, 1942
- Ixodes kingi Bishopp, 1911
- Ixodes (Scaphixodes) kohlsi Arthur, 1955b
- Ixodes kopsteini (Oudemans, 1926)
- Ixodes kuntzi Hoogstraal and Kohls, 1965a
- Ixodes laguri Olenev, 1929
- Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) lanigeri Hornok, 2024[49]
- Ixodes laridis Heath and Palma, 2017
- Ixodes lasallei Méndez Arocha and Ortiz, 1958
- Ixodes latus Arthur, 1958[39]
- Ixodes laysanensis Wilson, 1964a
- Ixodes lemuris Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes lewisi Arthur, 1965
- Ixodes lividus Koch, 1844
- Ixodes (Haemixodes) longiscutatus Boero, 1944
- Ixodes (Amerixodes) loricatus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes loveridgei Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes luciae Sénevet, 1940
- Ixodes lunatus Neumann, 1907
- Ixodes luxuriosus Schulze, 1935
- Ixodes macfarlanei Keirans, Clifford and Walker, 1982
- Ixodes malayensis Kohls, 1962
- Ixodes marmotae Cooley and Kohls, 1938
- Ixodes marxi Banks, 1908
- Ixodes maslovi Emel'yanova and Kozlovskaya, 1967
- Ixodes matopi Spickett, Keirans, Norval and Clifford, 1981
- Ixodes mexicanus Cooley and Kohls, 1942
- Ixodes microgalei Apanaskevich, Soarimalala and Goodman, 2013[50]
- Ixodes minor Neumann, 1902
- Ixodes minutae Arthur, 1959
- Ixodes mitchelli Kohls, Clifford and Hoogstraal, 1970
- Ixodes mirzai Apanaskevich & Schenk, 2020[36]
- Ixodes (Ixodes) mojavensis Backus & Beati, 2022[51]
- Ixodes monospinosus Saito, 1967
- Ixodes montoyanus Cooley, 1944
- Ixodes moreli Arthur, 1957
- Ixodes moscharius Teng, 1982
- Ixodes moschiferi Nemenz, 1968
- Ixodes muniensis Arthur and Burrow, 1957
- Ixodes muris Bishopp and Smith, 1937
- Ixodes murreleti Cooley and Kohls, 1945
- Ixodes myospalacis Teng, 1986
- Ixodes myotomys Clifford and Hoogstraal, 1970
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) myremecobii Roberts, 1962
- Ixodes nairobiensis Nuttall, 1916
- Ixodes nchisiensis Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes nectomys Kohls, 1956a
- Ixodes neitzi Clifford, Walker and Keirans, 1977
- Ixodes nesomys Uilenberg and Hoogstraal, 1969
- Ixodes neuquenensis Ringuelet, 1947
- Ixodes nicolasi Santos Dias, 1982
- Ixodes nipponensis Kitaoka and Saito, 1967
- Ixodes nitens Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes nuttalli Lahille, 1913
- Ixodes nuttallianus Schulze, 1930
- Ixodes occultus Pomerantzev, 1946
- Ixodes ochotonae Gregson, 1941
- Ixodes okapiae Arthur, 1956
- Ixodes oldi Nuttall, 1913
- Ixodes (Coxixodes) ornithorhynchi Lucas, 1846
- Ixodes (Partipalpiger) ovatus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes pacificus Cooley and Kohls, 1943
- Ixodes (Ixodes) paragibbosus Hornok and Kontschán, 2025[44]
- Ixodes paranaensis Barros-Battesti, Arzua, Pichorim and Keirans, 2003
- Ixodes pararicinus Keirans and Clifford, 1985
- Ixodes pavlovskyi Pomerantzev, 1946
- Ixodes percavatus Neumann, 1906
- Ixodes peromysci Auguston, 1940
- Ixodes persulcatus Schulze, 1930
- Ixodes petauristae Warburton, 1933
- Ixodes (Scaphixodes) philipi Keirans and Kohls, 1970
- Ixodes pilosus Koch, 1844
- Ixodes planiscutatus Apanaskevich & Schenk, 2020[36]
- Ixodes pomerantzevi Serdjukova, 1941
- Ixodes pomerantzi Kohls, 1956
- Ixodes priscicollaris Schulze, 1932
- Ixodes procaviae Arthur and Burrow, 1957
- Ixodes prokopjevi (Emel'yanova, 1979)
- Ixodes radfordi Kohls, 1948
- Ixodes rageaui Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes randrianasoloi Uilenberg and Hoogstraal, 1969b
- Ixodes rasus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes redikorzevi Olenev, 1927
- Ixodes rhabdomysae Arthur, 1959
- Ixodes ricinus (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Ixodes rothschildi Nuttall and Warburton, 1911
- Ixodes rotundatus Arthur, 1958
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) rubicundus Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes rubidus Neumann, 1901
- Ixodes rugicollis Schulze and Schlottke, 1929b
- Ixodes rugosus Bishopp, 1911
- Ixodes sachalinensis Filippova, 1971
- Ixodes scapularis Say, 1821
- Ixodes schillingsi Neumann, 1901
- Ixodes schulzei Aragão and Fonseca, 1951
- Ixodes sculptus Neumann, 1904
- Ixodes semenovi Olenev, 1929
- Ixodes shahi Clifford, Hoogstraal and Kohls, 1971
- Ixodes siamensis Kitaoka and Suzuki, 1983[52][53] [a]
- Ixodes sigelos Keirans, Clifford and Corwin, 1976
- Ixodes signatus Birula, 1895
- Ixodes (Trichotoixodes) silvanus Saracho-Bottero, Beati, Venzal, Guglielmone & Nava, 2021[54]
- Ixodes (Pomerantzevella) simplex Neumann, 1906
- Ixodes sinaloa Kohls and Clifford, 1966
- Ixodes sinensis Teng, 1977
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) soarimalalae Apanaskevich & Goodman, 2020[55]
- Ixodes soricis Gregson, 1942
- Ixodes spinae Arthur, 1958[39]
- Ixodes spinicoxalis Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes spinipalpis Hadwen and Nuttall, 1916
- Ixodes spinosus Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes steini Schulze, 1935
- Ixodes stellae Apanaskevich & Schenk, 2020[36]
- Ixodes stilesi Neumann, 1911
- Ixodes stromi Filippova, 1957
- Ixodes subterraneus Filippova, 1961
- Ixodes succineus Weidner, 1964
- Ixodes taglei Kohls, 1969
- Ixodes tamaulipas Kohls and Clifford, 1966
- Ixodes tancitarius Cooley and Kohls, 1942
- Ixodes tanuki Saito, 1964
- Ixodes tapirus Kohls, 1956
- Ixodes (Ixodes) tatei Arthur, 1959[44]
- Ixodes (Endopalpiger) tasmani Neumann, 1899
- Ixodes tecpanensis Kohls, 1956
- Ixodes texanus Banks, 1909
- Ixodes (Trichotoixodes) theilerae Arthur, 1953
- Ixodes thomasae Arthur and Burrow, 1957
- Ixodes tiptoni Kohls and Clifford, 1962
- Ixodes tovari Cooley, 1945
- Ixodes transvaalensis Clifford and Hoogstraal, 1966
- Ixodes (Filippoviella) trianguliceps Birula, 1895
- Ixodes (Sternalixodes) trichosuri Roberts, 1960
- Ixodes tropicalis Kohls, 1956a
- Ixodes (Trichotoixodes) turdus Nakatsudi, 1942
- Ixodes ugandanus Neumann, 1906
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) uilenbergi Apanaskevich & Goodman, 2020[55]
- Ixodes (Afrixodes) uncus Apanaskevich & Goodman, 2020[55]
- Ixodes unicavatus Neumann, 1908
- Ixodes (Ceratixodes) uriae White, 1852
- Ixodes vanidicus Schulze, 1943
- Ixodes venezuelensis Kohls, 1953
- Ixodes ventalloi Gill Collado, 1936
- Ixodes (Eschatocephalus) vespertilionis Koch, 1844
- Ixodes vestitus Neumann, 1908
- Ixodes victoriensis Nuttall, 1916
- Ixodes walkerae Clifford, Kohls and Hoogstraal, 1968
- Ixodes werneri Kohls, 1950
- Ixodes woodi Bishopp, 1911
- Ixodes (Endopalpiger) woyliei Ash, Elliot, Godfrey, Burmej, Abdad, Northover, Wayne, Morris, Clode, Lymbery and Thompson, 2017
- Ixodes zaglossi Kohls, 1960
- Ixodes (Ixodes) zacateco Apanaskevich & Bunn, 2025[56]
- Ixodes zairensis Keirans, Clifford and Walker, 1982
Fossil Species
[edit]
Three fossil species of Ixodes are known from amber deposits ranging from the Cretaceous to the Eocene:
- †Ixodes antiquorum Chitimia-Dobler, Mans and Dunlop, 2022 (Burmese amber, Cenomanian, ~ 99 Ma)[57]
- †Ixodes succineus Weidner, 1964 (Baltic amber, Eocene, ~ 49–44 Ma)[58][59]
- †Ixodes tertiarius Scudder, 1885 (Green River Formation, Eocene, 50 Ma)[60][61][b]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Sometimes listed as a synonym of I. ovatus
- ^ Ixodes tertiarius is a nomen dubium, and should be excluded from the fossil record
Additional Readings
[edit]Refer to the following external links for recent changes to Ixodes taxonomy:
- Guglielmone, A. A., Robbins, R. G., Apanaskevich, D. A., Petney, T. N., Estrada-Peña, A., & Horak, I. G. (2014a). The Hard Ticks of the World: (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7497-1
- Guglielmone, A.A., Petney, T.N. & Robbins, R.G. (2020) Ixodidae (Acari: Ixodoidea): descriptions and redescriptions of all known species from 1758 to December 31, 2019. Zootaxa, 4871 (1), 1–322. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4871.1.1
References
[edit]- ^ Valeria Castilho Onofrio; Darci Moraes Barros-Battesti; Marcelo Bahia Labruna; João Luiz Horácio Faccini (2009). "Diagnoses of and illustrated key to the species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae) from Brazil". Systematic Parasitology. 72 (2): 143–157. doi:10.1007/s11230-008-9169-z. PMID 19115087. S2CID 19483827.
- ^ Deane Philip Furman; Edmond C. Loomis (1984). "Genus Ixodes Latreille". The Ticks of California (Acari: Ixodida). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey. Vol. 25. University of California Press. pp. 47–77. ISBN 978-0-520-09685-1.
- ^ Fisher, Bruce; Harvey, Richard P.; Champe, Pamela C. (2007). Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews: Microbiology (Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews Series). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 334. ISBN 978-0-7817-8215-9.
- ^ Estrada-Peña, Agustín; Guglielmone, Alberto A.; Nava, Santiago (2023-02-21). "Worldwide host associations of the tick genus Ixodes suggest relationships based on environmental sharing rather than on co-phylogenetic events". Parasites & Vectors. 16 (1): 75. doi:10.1186/s13071-022-05641-9. ISSN 1756-3305. PMID 36810195.
- ^ Barker, Stephen C.; Barker, Dayana (2023-03-08). "Ticks of Australasia: 125 species of ticks in and around Australia". Zootaxa. 5253 (1): 1–670. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5253.1.1. ISSN 1175-5334. PMID 37044756.
- ^ Barker, Stephen C.; Kelava, Samuel; Mans, Ben J.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Seeman, Owen D.; Gofton, Alexander; Shao, Renfu; Teo, Ernest J. M.; Evasco, Kimberley L.; Soennichsen, Kari F.; Barker, Dayana; Nakao, Ryo (2024-02-12). "The first cryptic genus of Ixodida, Cryptocroton n. gen. for Amblyomma papuanum Hirst, 1914: a tick of North Queensland, Australia, and Papua New Guinea". Zootaxa. 5410 (1): 91–111. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5410.1.5. ISSN 1175-5334.
- ^ Guglielmone, Alberto A.; Petney, Trevor N.; Robbins, Richard G. (2020-11-05). "Ixodidae (Acari: Ixodoidea): descriptions and redescriptions of all known species from 1758 to December 31, 2019". Zootaxa. 4871 (1): 1–322. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4871.1.1. ISSN 1175-5334.
- ^ a b c Barker, Dayana; Seeman, Owen D.; Barker, Stephen C. (2021-09-20). "The development of tick taxonomy and systematics in Australia and Papua New Guinea through the works of five late 20th century contributors and with comments on the place of Australasia in the study of the phylogeny and evolution of the ticks". Systematic and Applied Acarology: 1793–1832. doi:10.11158/saa.26.10.1. ISSN 2056-6069.
- ^ Barker, Dayana; Kelava, Samuel; Seeman, Owen D.; Shao, Renfu; Seaniger, James R.; Jones, Malcolm K.; Apanaskevich, Maria A.; Nakao, Ryo; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Barker, Stephen C. (2022-08-01). "Rediscovery of Ixodes confusus in Australia with the first description of the male from Australia, a redescription of the female and the mitochondrial (mt) genomes of five species of Ixodes". International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife. 18: 1–11. Bibcode:2022IJPPW..18....1B. doi:10.1016/j.ijppaw.2022.03.006. ISSN 2213-2244. PMC 8971345. PMID 35371916.
- ^ Barker, Stephen C.; Kelava, Samuael; Heath, Allen C. G.; Seeman, Owen D.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Mans, Ben J.; Shao, Renfu; Gofton, Alexander W.; Teo, Ernest J. M.; Byrne, Andrew F.; Ito, Takuya; Tan, Craig J.; Barker, Dayana; Nakao, Ryo (2023-08-10). "A new subgenus, Australixodes n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae), for the kiwi tick, Ixodes anatis Chilton, 1904, and validation of the subgenus Coxixodes Schulze, 1941 with a phylogeny of 16 of the 22 subgenera of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 from entire mitochondrial genome sequences". Zootaxa. 5325 (4): 529–540. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5325.4.4. ISSN 1175-5334. PMID 38220895.
- ^ Morel, P. C. (1966). Sur quelques larves d'Ixodes Latreille, 1796, d'Afrique (Acariens, Ixodoidea). Acarologia, 8, 208-221.
- ^ Cerny, V. (1969). Institute of Parasitology, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague. Folia Parasitologica (PRAHA), 16, 279-284.
- ^ a b Camicas, J. L., Hervy, J. P., Adam, F., & Morel, P. C. (1998). The ticks of the world (Acarida, Ixodida): nomenclature, described stages, hosts, distribution.
- ^ a b Barker, Stephen C.; Kelava, Samuael; Heath, Allen C. G.; Seeman, Owen D.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Mans, Ben J.; Shao, Renfu; Gofton, Alexander W.; Teo, Ernest J. M.; Byrne, Andrew F.; Ito, Takuya; Tan, Craig J.; Barker, Dayana; Nakao, Ryo (2023-08-10). "A new subgenus, Australixodes n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae), for the kiwi tick, Ixodes anatis Chilton, 1904, and validation of the subgenus Coxixodes Schulze, 1941 with a phylogeny of 16 of the 22 subgenera of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 from entire mitochondrial genome sequences". Zootaxa. 5325 (4): 529–540. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5325.4.4. ISSN 1175-5334.
- ^ Neumann, L.G., 1902. Mém. Soc. Zool. France, 15:125–130
- ^ Schulze, P., 1935. Zur vergleichenden anatomie der zecken. (Das sternale, die mundwerkzeuge, analfurchen und analbeschilderung, ihre bedeutung, ursprünglichkeit und luxurieren.). Zeitschrift für Morphologie und ¨Okologie der Tiere 30, 1–40
- ^ Frauenfeld, G. (1853). Eschatocephalus gracilipes. Verhandlungen des KK.
- ^ Filippova, N. A. (2010-09-01). "Uncommon zoogeographical connections in the subgenus Exopalpiger Schultze of the genus Ixodes Latreille (Acari, Ixodidae)". Entomological Review. 90 (6): 793–797. Bibcode:2010EntRv..90..793F. doi:10.1134/S0013873810060151. ISSN 1555-6689.
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Greiman, Stephen E.; Fedorov, Denis S.; Ahmed, Rokeya; Barker, Stephen C. (2024-04-22). "A new subgenus of hard ticks, Filippoviella n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae) comprising Ixodes trianguliceps Birula, 1895 and I. ghilarovi Filippova & Panova, 1988, parasites of small mammals in Europe and Asia". Zootaxa. 5443 (2): 224–236. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5443.2.5. ISSN 1175-5334.
- ^ IRMNG: Haemixodes Kohls & Clifford 1967
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Greiman, Stephen E.; Fedorov, Denis S.; Ahmed, Rokeya; Barker, Stephen C. (2024-04-22). "A new subgenus of hard ticks, Filippoviella n. subgen. (Acari: Ixodidae) comprising Ixodes trianguliceps Birula, 1895 and I. ghilarovi Filippova & Panova, 1988, parasites of small mammals in Europe and Asia". Zootaxa. 5443 (2): 224–236. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5443.2.5. ISSN 1175-5334.
- ^ Filippova, IN. A. 1957. Ixodes stromi, new species of tick and its systematic position in Ixodinae. Zool. Zh.36: 864-869 (in Russian, with English summary [English translation: NAMRU-3-T69]).
- ^ Robbins, Richard G.; Keirans, James E. (1987-05-01). "Ixodes (Ixodiopsis) woodi (Acari: Ixodidae): Description of the Larva and Redescription of the Nymph". Journal of Medical Entomology. 24 (3): 310–314. doi:10.1093/jmedent/24.3.310. ISSN 1938-2928. PMID 3585925.
- ^ Clifford, Carleton M.; Sonenshine, Daniel E.; Keirans, James E.; Kohls, Glen M. (1973-05-15). "Systematics of the Subfamily Ixodinae (Acarina: Ixodidae). 1. the Subgenera of Ixodes". Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 66 (3): 489–500. doi:10.1093/aesa/66.3.489. ISSN 1938-2901.
- ^ Filippova NA. 1977. Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodinae. Leningrad: Izd. Nauka, 393 pp. (In Russian)
- ^ Emelyanova, N. D., & Kozlovskaya, O. L. (1968). A NEW SPECIES AND SUBGENUS OF THE GENUS IXODES LATR. (PARASITIFORMES, IXODIDAE) FROM THE FAR EAST OF U.S.S.R.
- ^ Neumann, L.G. (1904) Notes sur les ixodidés. II. Archives de Parasitologie, 8, 444–464.
- ^ Hoogstraal, Harry; Clifford, Carleton M.; Saito, Yutaka; Keirans, James E. (1973-04-25). "Ixodes (Partipalpiger) Ovatus Neumann, Subgen. Nov.: Identity, Hosts, Ecology, and Distribution (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae)1". Journal of Medical Entomology. 10 (2): 157–164. doi:10.1093/jmedent/10.2.157. ISSN 1938-2928. PMID 4732945.
- ^ Krumpálová, Zuzana; Mangová, Barbara; Purgatová, Slávka; Didyk, Yuliya M.; Kazimírová, Mária (2023-04-21). "Molecular characterisation of three Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) species (Ixodida, Ixodidae) and the first record of Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) kaiseri from Slovakia". ZooKeys (1158): 147–162. Bibcode:2023ZooK.1158..147K. doi:10.3897/zookeys.1158.101936. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 10193145. PMID 37215694.
- ^ M., Clifford, Carleton; E., Sonenshine, Daniel; E., Keirans, James; M., Kohls, Glen (1973-05-15). "Systematics of the Subfamily Ixodinae (Acarina: Ixodidae). 1. the Subgenera of Ixodes". Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 66 (3). doi:10.1093/ae (inactive 20 October 2025). ISSN 0013-8746. Archived from the original on 2021-03-08.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of October 2025 (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Feider, Z. 1965. Acaromorpha Superfamilia Ixodoidea. In Fauna Republicii Populare Romane, Arachnida vol. 4:1-406
- ^ Schulze, P. (1941). "Das Geruchsorgan Der Zecken. Untersuchungen Über Die Abwandlungen Eines Sinnesorgans Und Seine Stammesgeschichtliche Bedeutung". Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere. 37 (3): 491–564. doi:10.1007/BF00408327. ISSN 0372-9389. JSTOR 43261795.
- ^ Reznik, P.A., 1961. Contribution to study of immature stages of the tick family Ixodidae. Communication six. Description of Ixodes frontalis Panz. larvae and nymphs and Ixodes redikorzevi Ol. larvae. Tr. Nauchno-Issled. Protivochumnogo Inst. Kavk. Zakavk. 5, 276–286
- ^ Schulze, P. (1941). "Das Geruchsorgan Der Zecken. Untersuchungen Über Die Abwandlungen Eines Sinnesorgans Und Seine Stammesgeschichtliche Bedeutung". Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere. 37 (3): 491–564. doi:10.1007/BF00408327. ISSN 0372-9389. JSTOR 43261795.
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A. (2024-07-02). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), parasite of rodents (Rodentia: Muridae) in Malaysia and Vietnam". Systematic Parasitology. 101 (4) 48. doi:10.1007/s11230-024-10172-1. ISSN 1573-5192.
- ^ a b c d e Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Schenk, John J. (2020). "Description of five new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae) and redescription of I. luxuriosus Schulze, 1935, I. steini Schulze, 1935 and I. zaglossi Kohls, 1960, parasites of marsupials, rodents and echidnas in New Guinea Island". Systematic Parasitology. 97 (3): 223–266. doi:10.1007/s11230-020-09909-5. PMID 32328810. S2CID 216085891.
- ^ Aftisse, Lydia; Merabet, Samira; Keskin, Adem; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A. (2024-11-17). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), a parasite of rodents (Rodentia: Muridae) in Algeria". Systematic Parasitology. 102 (1): 5. doi:10.1007/s11230-024-10197-6. ISSN 1573-5192. PMID 39551907.
- ^ Englert, Mackenzie C.; Goodman, Steven M.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A. (2023-12-01). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), parasite of shrew tenrecs (Afrotheria: Tenrecidae) and rodents (Rodentia: Muridae) on Madagascar". Systematic Parasitology. 100 (6): 745–750. doi:10.1007/s11230-023-10122-3. ISSN 1573-5192.
- ^ a b c d Arthur, Don Ramsay (1958). "New species of Ixodes ticks from eastern Africa, with a description of the male and nymph of Ixodes oldi Nuttall, 1913". Parasitology. 48 (1–2): 38–69. doi:10.1017/S0031182000021053. PMID 13566853.
- ^ Barker, Dayana (2019). "Ixodes barkeri n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae) from the short-beaked echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus, with a revised key to the male Ixodes of Australia, and list of the subgenera and species of Ixodes known to occur in Australia". Zootaxa. 4658 (2): 331–342. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4658.2.7. PMID 31716747. S2CID 202031409.
- ^ Keirans, James E.; Lacombe, Eleanor H. (1998). "First Records of Amblyomma americanum, Ixodes (Ixodes) dentatus, and Ixodes (Ceratixodes) uriae (Acari: Ixodidae) from Maine". The Journal of Parasitology. 84 (3). [The American Society of Parasitologists, Allen Press]: 629–631. doi:10.2307/3284739. JSTOR 3284739.
- ^ Barker, Dayana; Kelava, Samuel; Seeman, Owen D.; Shao, Renfu; Seaniger, James R.; Jones, Malcolm K.; Apanaskevich, Maria A.; Nakao, Ryo; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Barker, Stephen C. (2022-08-01). "Rediscovery of Ixodes confusus in Australia with the first description of the male from Australia, a redescription of the female and the mitochondrial (mt) genomes of five species of Ixodes". International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife. 18: 1–11. Bibcode:2022IJPPW..18....1B. doi:10.1016/j.ijppaw.2022.03.006. ISSN 2213-2244. PMC 8971345. PMID 35371916.
- ^ Contini, C.; Palmas, C.; Seu, V.; Stancampiano, L.; Usai, F. (2011). "Redescription of the male of Ixodes festai Rondelli, 1926 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) on specimens from Sardinia (Italy)". Parasite. 18 (3): 235–240. doi:10.1051/parasite/2011183235. PMC 3671470. PMID 21894264.

- ^ a b c Hornok, Sándor; Keskin, Adem; Uspensky, Igor; Kontschán, Jenő; Takács, Nóra; Lesiczka, Paulina; Warbroek, Tim; van den Bosch, Tijs J. M.; Keve, Gergő; Pitó, Andor; Sándor, Attila D. (2025-09-19). "Updates on subgenus Ixodes in the Mediterranean region: validity of Ixodes festai Rondelli, 1926, reinstatement of Ixodes tatei Arthur, 1959, and a new species closely related to Ixodes gibbosus Nuttall, 1916". International Journal for Parasitology. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2025.09.002. ISSN 0020-7519.
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Lemon, Howard E. (2018). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae) and redescription of I. priscicollaris Schulze, 1932, parasites of New Guinea rodents (Rodentia: Muridae)". Systematic Parasitology. 95 (4): 373–382. doi:10.1007/s11230-018-9786-0. PMID 29536248. S2CID 4504691.
Ixodes goliath n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae), is described based on females collected from the eastern hyomys, Hyomys goliath (Milne-Edwards) (Rodentia: Muridae) from Papua New Guinea.
- ^ Kwak, M. L.; Madden, C.; Wicker, L. (2018). "Ixodes heathi n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae), a co-endangered tick from the critically endangered mountain pygmy possum (Burramys parvus), with notes on its biology and conservation". Experimental and Applied Acarology. 76 (3): 413–419. doi:10.1007/s10493-018-0312-5. PMID 30302626. S2CID 52945250.
A new species of co-endangered tick, Ixodes heathi n. sp., is described from specimens of the nymph collected on the critically endangered mountain pygmy possum (Burramys parvus Broom) from the alpine region of Victoria, Australia. Its biology is discussed along with strategies for its conservation.
- ^ Duan, De-Yong; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Liu, Lei; Liu, Guo-Hua; Cheng, Tian-Yin (2022). "Identification of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), parasite of hog badgers (Carnivora: Mustelidae) in China". Medical and Veterinary Entomology. 36 (4): 444–455. doi:10.1111/mve.12582. ISSN 1365-2915. PMID 35588433.
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Drew, Carley E.; Pienaar, Ronel (2025-08-27). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae) and notes on I. spinae Arthur, 1958, parasites of the rock hyrax, Procavia capensis (Pallas) (Hyracoidea: Procaviidae) in South Africa". Systematic Parasitology. 102 (5): 53. doi:10.1007/s11230-025-10248-6. ISSN 1573-5192.
- ^ Hornok, Sándor; Kontschán, Jenő; Takano, Ai; Gotoh, Yasuhiro; Hassanin, Alexandre; Tu, Vuong Tan (2024-10-14). "Description of Ixodes lanigeri sp. nov., a new hard tick species (Acari, Ixodidae) collected from mouse-eared bats (Vespertilionidae, Myotis) in Vietnam". ZooKeys (1215): 107–125. Bibcode:2024ZooK.1215..107H. doi:10.3897/zookeys.1215.123624. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 11494211. PMID 39440030.
- ^ Apanaskevich, D. A.; Soarimalala, V.; Goodman, S. M. (2013). "A new Ixodes species (Acari: Ixodidae), parasite of shrew tenrecs (Afrosoricida: Tenrecidae) in Madagascar". Journal of Parasitology. 99 (6): 970–972. doi:10.1645/13-306.1. PMC 4833386. PMID 23901784.
- ^ Backus, Laura H.; Foley, Janet E.; Hobbs, Guy B.; Bai, Ying; Beati, Lorenza (2022-11-01). "A new species of tick, Ixodes (Ixodes) mojavensis (Acari: Ixodidae), from the Amargosa Valley of California". Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases. 13 (6) 102020. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.102020. ISSN 1877-959X. PMC 10917073. PMID 35987116.
- ^ Kitaoka, Shigeo; Suzuki, Hiroshi (1983). "Studies on the Parasite Fauna of Thailand: 5. Parasitic ticks on mammals and description of Ixodes siamensis sp. n. and Rhipicephalus tetracornus sp. n. (Acarina: Ixodidae)". Tropical Medicine. 25 (4): 205–219. hdl:10069/4366.
Ixodes siamensis sp. n. is the second species of the subgenus Paltipalpiger.
- ^ Guglielmone, Alberto A.; Robbins, Richard G.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Petney, Trevor N.; Estrada-Peña, Agustín; Horak, Ivan G. (2009). "Comments on controversial tick (Acari: Ixodida) species names and species described or resurrected from 2003 to 2008". Experimental and Applied Acarology. 48 (4): 311–327. doi:10.1007/s10493-009-9246-2. hdl:2263/13757. PMID 19169832. S2CID 29053875.
We consider the following 40 names valid…Ixodes siamensis Kitaoka and Suzuki, 1983.
- ^ Bottero, Maria N. Saracho; Beati, Lorenza; Venzal, José M.; Guardia, Leonor; Thompson, Carolina S.; Mangold, Atilio J.; Guglielmone, Alberto A.; Nava, Santiago (2021-01-01). "Ixodes silvanus n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae), a new member of the subgenus Trichotoixodes Reznik, 1961 from northwestern Argentina". Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases. 12 (1) 101572. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101572. ISSN 1877-959X. PMID 33068841.
- ^ a b c Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Goodman, Steven M. (2020-12-01). "Description of three new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), parasites of tenrecs (Afrotheria: Tenrecidae) on Madagascar". Systematic Parasitology. 97 (6): 623–637. doi:10.1007/s11230-020-09944-2. ISSN 1573-5192.
- ^ Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Bunn, Kennedy G. (2025-07-19). "Description of a new species of Ixodes Latreille, 1795 (Acari: Ixodidae), parasite of the Mexican spiny pocket mouse, Heteromys irroratus Gray (Rodentia: Heteromyidae) in Mexico". Systematic Parasitology. 102 (4): 46. doi:10.1007/s11230-025-10245-9. ISSN 1573-5192. PMID 40682685.
- ^ Chitimia-Dobler, Lidia; Mans, Ben J.; Handschuh, Stephan; Dunlop, Jason A. (2022). "A remarkable assemblage of ticks from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber". Parasitology. 149 (6): 820–830. doi:10.1017/S0031182022000269. ISSN 0031-1820. PMID 35241194.
- ^ Dunlop, Jason A.; Apanaskevich, Dmitry A.; Lehmann, Jens; Hoffmann, René; Fusseis, Florian; Ehlke, Moritz; Zachow, Stefan; Xiao, Xianghui (2016-10-10). "Microtomography of the Baltic amber tick Ixodes succineus reveals affinities with the modern Asian disease vector Ixodes ovatus". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 16 (1): 203. Bibcode:2016BMCEE..16..203D. doi:10.1186/s12862-016-0777-y. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 5057450. PMID 27724841.
- ^ Weidner H. Eine Zecke, Ixodes succineus sp. n., im baltischen Bernstein. Veröffent Übersee-Mus Bremen. 1964;3:143–51
- ^ Dunlop, J.A. (2011-12-20). "The fate and status of the supposed fossil tick Ixodes tertiarius Scudder, 1885". Acarologia. 51 (4): 399–404. doi:10.1051/acarologia/20112021. ISSN 0044-586X.
- ^ Scudder S. H. 1885 — 3. Classe. Arachnoidea. Spinnen. Skorpione. — In: Zittel, K. A. (Ed.) Handbuch der Palaeontologie. I. Abtheilung. Palaeozoologie 2. München & Leipzig: R. Oldenbourg. p. 732-746.

