INTS7
المظهر
| INTS7 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معرفات | |||||||||||||||||
| أسماء بديلة | INTS7, C1orf73, INT7, integrator complex subunit 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| معرفات خارجية | الوراثة المندلية البشرية عبر الإنترنت 611350 MGI: MGI:1924315 HomoloGene: 9136 GeneCards: 25896 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| نمط التعبير عن الحمض النووي الريبوزي | |||||||||||||||||
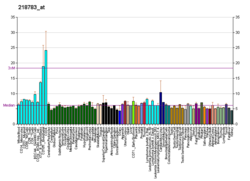 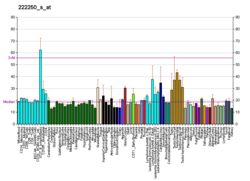 |
|||||||||||||||||
| المزيد من بيانات التعبير المرجعية | |||||||||||||||||
| تماثلات متسلسلة | |||||||||||||||||
| أنواع | الإنسان | الفأر | |||||||||||||||
| أنتريه | 25896 | 77065 | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000143493 | ENSMUSG00000037461 | |||||||||||||||
| يونيبروت | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (رنا مرسال.) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (بروتين) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| الموقع (UCSC | n/a | Chr 1: 191.31 – 191.36 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| بحث ببمد | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||||
| ويكي بيانات | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
INTS7 (Integrator complex subunit 7) هوَ بروتين يُشَفر بواسطة جين INTS7 في الإنسان.[1][2]
الوظيفة
[عدل]هذا القسم فارغ أو غير مكتمل. ساهم في توسيعه. (يوليو 2018) |
الأهمية السريرية
[عدل]هذا القسم فارغ أو غير مكتمل. ساهم في توسيعه. (يوليو 2018) |
المراجع
[عدل]- ^ "Entrez Gene: INTS7 integrator complex subunit 7". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2010-12-05.
- ^ Baillat D، Hakimi MA، Naar AM، Shilatifard A، Cooch N، Shiekhattar R (أكتوبر 2005). "Integrator, a multiprotein mediator of small nuclear RNA processing, associates with the C-terminal repeat of RNA polymerase II". Cell. ج. 123 ع. 2: 265–76. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.019. PMID:16239144.
قراءة متعمقة
[عدل]- Mehrle A، Rosenfelder H، Schupp I، وآخرون (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. ج. 34 ع. Database issue: D415–8. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC:1347501. PMID:16381901.
- Wiemann S، Arlt D، Huber W، وآخرون (2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Res. ج. 14 ع. 10B: 2136–44. DOI:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC:528930. PMID:15489336.
- Gerhard DS، Wagner L، Feingold EA، وآخرون (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. ج. 14 ع. 10B: 2121–7. DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC:528928. PMID:15489334.
- Ota T، Suzuki Y، Nishikawa T، وآخرون (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. ج. 36 ع. 1: 40–5. DOI:10.1038/ng1285. PMID:14702039.
- Strausberg RL، Feingold EA، Grouse LH، وآخرون (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 99 ع. 26: 16899–903. DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC:139241. PMID:12477932.
- Wiemann S، Weil B، Wellenreuther R، وآخرون (2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Res. ج. 11 ع. 3: 422–35. DOI:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC:311072. PMID:11230166.
- Hartley JL، Temple GF، Brasch MA (2001). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Res. ج. 10 ع. 11: 1788–95. DOI:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC:310948. PMID:11076863.
