Hyperbolic functions
Appearance

Hyperbolic functions are different versions of trigonometric functions. They are defined using a hyperbola instead of a circle. Also, as the derivatives of sin(t) and cos(t) are cos(t) and –sin(t), the derivatives of sinh(t) and cosh(t) are cosh(t) and sinh(t).
The basic hyperbolic functions are:[1]
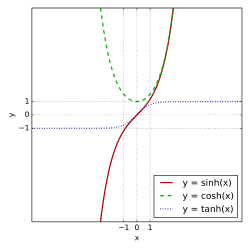
- hyperbolic sine "sinh" (/ˈsɪŋ, ˈsɪntʃ, ˈʃaɪn/),[2]
- hyperbolic cosine "cosh" (/ˈkɒʃ, ˈkoʊʃ/),
Using these, you can get:[3]
- hyperbolic tangent "tanh" (/ˈtæŋ, ˈtæntʃ, ˈθæn/),
- hyperbolic cotangent "coth" (/ˈkɒθ, ˈkoʊθ/),
- hyperbolic secant "sech" (/ˈsɛtʃ, ˈʃɛk/),
- hyperbolic cosecant "csch" or "cosech" (/ˈkoʊsɛtʃ, ˈkoʊʃɛk/)
and these have similar logic to the normal trigonometric functions.
The inverse hyperbolic functions are:
- inverse hyperbolic sine "arsinh" (also "sinh−1", "asinh" or sometimes "arcsinh")[4][5]
- inverse hyperbolic cosine "arcosh" (also "cosh−1", "acosh" or sometimes "arccosh")
- inverse hyperbolic tangent "artanh" (also "tanh−1", "atanh" or sometimes "arctanh")
- inverse hyperbolic cotangent "arcoth" (also "coth−1", "acoth" or sometimes "arccoth")
- inverse hyperbolic secant "arsech" (also "sech−1", "asech" or sometimes "arcsech")
- inverse hyperbolic cosecant "arcsch" (also "arcosech", "csch−1", "cosech−1","acsch", "acosech", or sometimes "arccsch" or "arccosech")
Definitions
[change | change source]
With hyperbolic angle u, the hyperbolic functions sinh and cosh can be defined using the exponential function eu.[1][3] In the figure .
Exponential definitions
[change | change source]

- Hyperbolic sine: the odd part of the exponential function, that is,
- Hyperbolic cosine: the even part of the exponential function, that is,

- Hyperbolic tangent:
- Hyperbolic cotangent: for x ≠ 0,
- Hyperbolic secant:
- Hyperbolic cosecant: for x ≠ 0,
Related pages
[change | change source]References
[change | change source]- 1 2 Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbolic Functions". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-08-29. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name ":1" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ (1999) Collins Concise Dictionary, 4th edition, HarperCollins, Glasgow, ISBN 0 00 472257 4, p. 1386
- 1 2 "Hyperbolic Functions". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-08-29. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name ":2" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Woodhouse, N. M. J. (2003), Special Relativity, London: Springer, p. 71, ISBN 978-1-85233-426-0
- ↑ Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene A., eds. (1972), Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 978-0-486-61272-0
- Osborn, G. (July 1902). "Mnemonic for hyperbolic formulae". The Mathematical Gazette. 2 (34): 189. doi:10.2307/3602492. JSTOR 3602492. S2CID 125866575.







