Cellular architecture
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
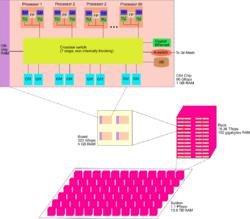
Cellular architecture is a type of computer architecture associated with parallel computing. It extends multi-core architecture by organizing processing into independent "cells," where each cell contains thread units, memory, and communication links. This design enables large numbers of concurrent threads to run within a single processor, with performance gains achieved through thread-level parallelism.
The most commercially recognized implementation was IBM's Cell microprocessor, a nine-core design used in the PlayStation 3 (2006–2017).[1] Another example was Cyclops64, a massively parallel research architecture developed by IBM in the 2000s.
Cellular architectures follow a low-level programming paradigm, exposing the programmer to much of the underlying hardware. This allows for fine-grained optimization but makes software development more complex.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Cell Designer talks about PS3 and IBM Cell Processors". Archived from the original on August 21, 2006. Retrieved March 22, 2007.
- ^ "What is a Low Level Language?". GeeksforGeeks. 2023-11-19. Retrieved 2025-03-25.
